Chloroquine is a potent inhibitor of SARS coronavirus infection and spread

NIH - HUMAN SYNTHESIS - 02 Oct 2021 (or EPUB)
Abstract
Background: Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a newly discovered coronavirus (SARS-CoV). No effective prophylactic or post-exposure therapy is currently available.
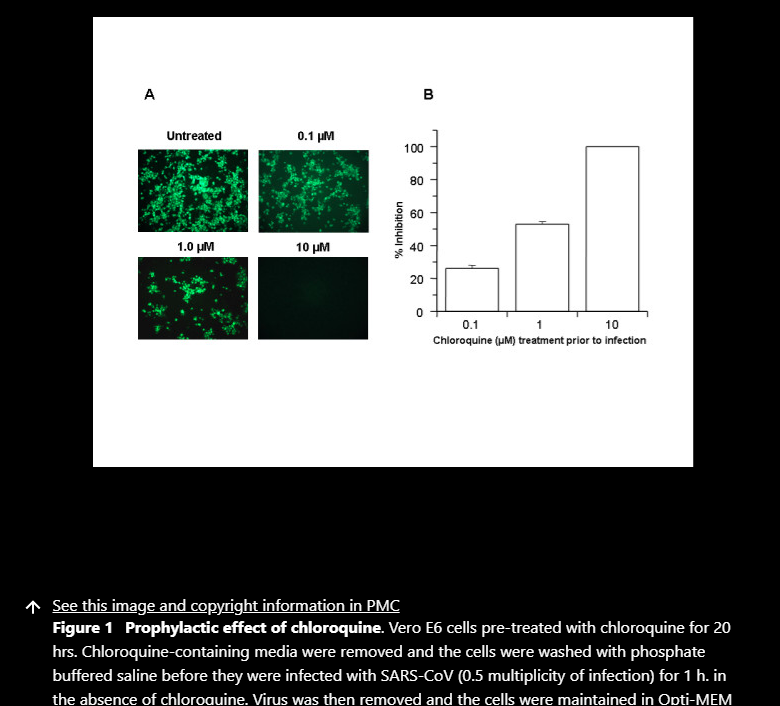
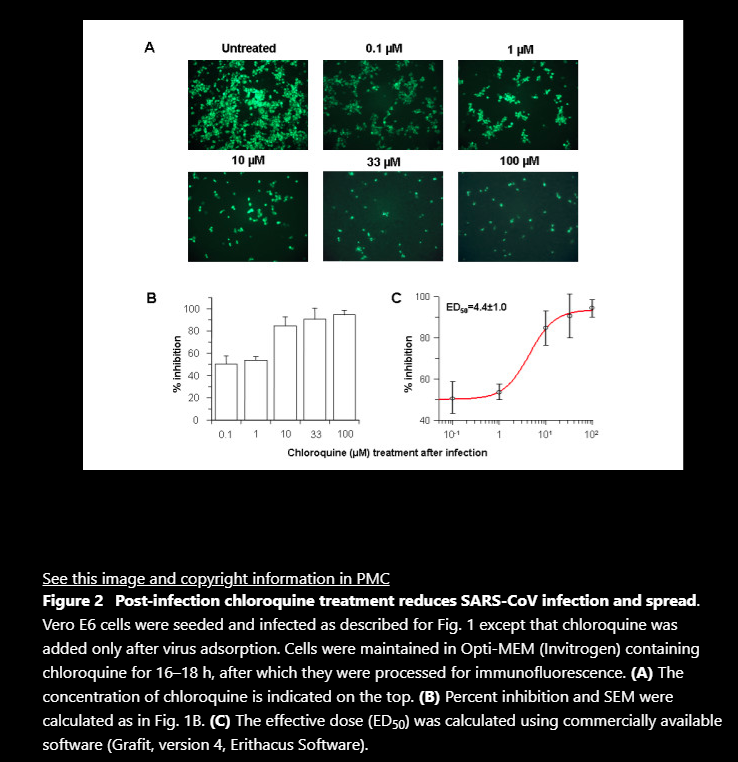
Results: We report, however, that chloroquine has strong antiviral effects on SARS-CoV infection of primate cells. These inhibitory effects are observed when the cells are treated with the drug either before or after exposure to the virus, suggesting both prophylactic and therapeutic advantages. In addition to the well-known functions of chloroquine such as elevations of endosomal pH, the drug appears to interfere with terminal glycosylation of the cellular receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. This may negatively influence the virus-receptor binding and abrogate the infection, with further ramifications by the elevation of vesicular pH, resulting in the inhibition of infection and spread of SARS CoV at clinically admissible concentrations.
Conclusion: Chloroquine is effective in preventing the spread of SARS CoV in cell culture. Favorable inhibition of virus spread was observed when the cells were either treated with chloroquine prior to or after SARS CoV infection. In addition, the indirect immunofluorescence assay described herein represents a simple and rapid method for screening SARS-CoV antiviral compounds.
Martin J Vincent 1, Eric Bergeron, Suzanne Benjannet, Bobbie R Erickson, Pierre E Rollin, Thomas G Ksiazek, Nabil G Seidah, Stuart T Nichol Affiliations expand.
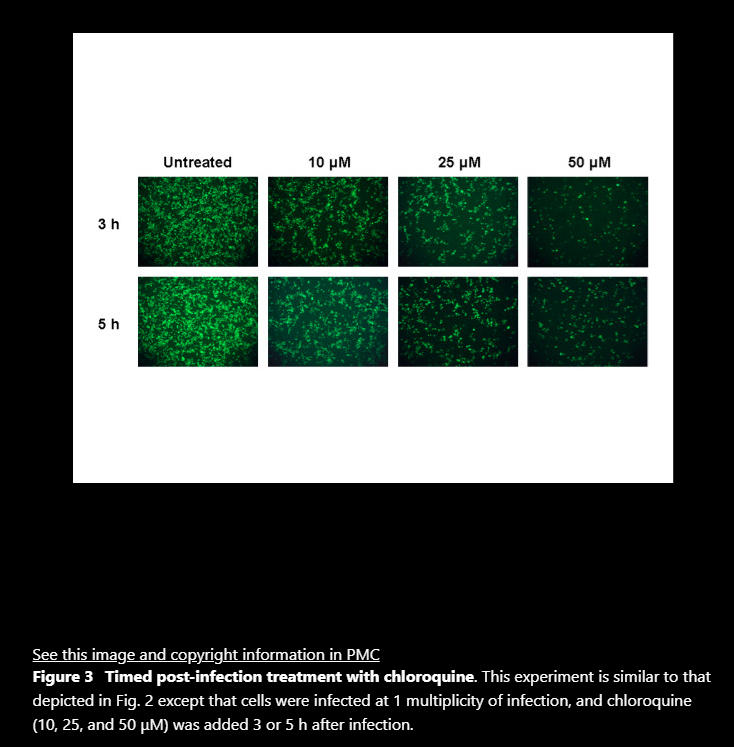
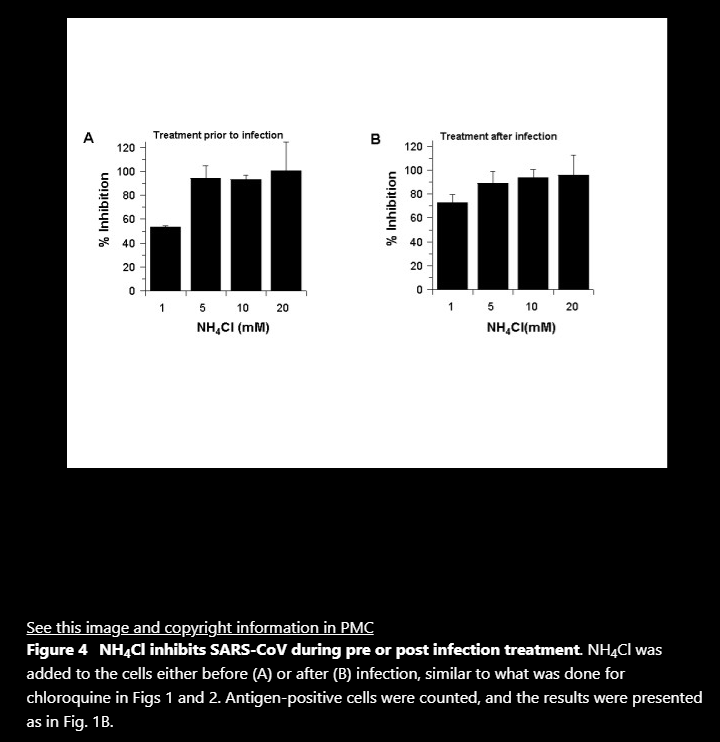
Figures
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry as a target of antiviral therapies.Kuhn JH, Li W, Radoshitzky SR, Choe H, Farzan M.Antivir Ther. 2007;12(4 Pt B):639-50.PMID: 17944271 Review.
- Efficient activation of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein by the transmembrane protease TMPRSS2.Matsuyama S, Nagata N, Shirato K, Kawase M, Takeda M, Taguchi F.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12658-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01542-10. Epub 2010 Oct 6.PMID: 20926566 Free PMC article.
- Identification of critical determinants on ACE2 for SARS-CoV entry and development of a potent entry inhibitor.Han DP, Penn-Nicholson A, Cho MW.Virology. 2006 Jun 20;350(1):15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.01.029. Epub 2006 Feb 28.PMID: 16510163 Free PMC article.
- In vitro inhibition of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus by chloroquine.Keyaerts E, Vijgen L, Maes P, Neyts J, Van Ranst M.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Oct 8;323(1):264-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.085.PMID: 15351731 Free PMC article.
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV--a target for vaccine and therapeutic development.Du L, He Y, Zhou Y, Liu S, Zheng BJ, Jiang S.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Mar;7(3):226-36. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2090. Epub 2009 Feb 9.PMID: 19198616 Free PMC article. Review.See all similar articles
Cited by 801 articles
- Feline Coronavirus Antivirals: A Review.Delaplace M, Huet H, Gambino A, Le Poder S.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 7;10(9):1150. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091150.PMID: 34578182 Free PMC article. Review.
- The strategy for controlling COVID-19 in Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG)/Iraq: Identification, epidemiology, transmission, treatment, and recovery.Aziz PY, Hadi JM, Sha AM, Aziz SB, Rahman HS, Ahmed HA, Abdulla MA, Amine Ali SM.Int J Surg Open. 2020;25:41-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijso.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jun 30.PMID: 34568609 Free PMC article.
- Discovery of potential SARS-CoV 3CL protease inhibitors from approved antiviral drugs using: virtual screening, molecular docking, pharmacophore mapping evaluation and dynamics simulation.Daoud I, Mesli F, Melkemi N, Ghalem S, Salah T.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Sep 20:1-18. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1973563. Online ahead of print.PMID: 34541995 Free PMC article.
- The association between malaria prevalence and COVID-19 mortality.Anyanwu MU.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 19;21(1):975. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06701-8.PMID: 34538242 Free PMC article.
- Hydroxychloroquine / azithromycin in COVID-19: The association between time to treatment and case fatality rate.Accinelli RA, Ynga-Meléndez GJ, León-Abarca JA, López LM, Madrid-Cisneros JC, Mendoza-Saldaña JD.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 14;44:102163. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102163. Online ahead of print.PMID: 34534686 Free PMC article.See all "Cited by" articles
References
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, Tong S, Urbani C, Comer JA, Lim W, Rollin PE, Dowell SF, Ling AE, Humphrey CD, Shieh WJ, Guarner J, Paddock CD, Rota PB, Fields B, DeRisi J, Yang JY, Cox N, Hughes J, LeDuc JW, Bellini WJ, Anderson LJ, SARS Working Group A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030781. - DOI - PubMed
- Marra MA, Jones SJ, Astell CR, Holt RA, Brooks-Wilson A, Butterfield YS, Khattra J, Asano JK, Barber SA, Chan SY, Cloutier A, Coughlin SM, Freeman D, Girn N, Griffith OL, Leach SR, Mayo , McDonald H, Montgomery SB, Pandoh PK, Petrescu AS, Robertson AG, Schein JE, Siddiqui A, Smailus DE, Stott JM, Yang GS, Plummer F, Andonov A, Artsob H, Bastien N, Bernard K, Booth TF, Bowness D, Czub M, Drebot M, Fernando L, Flick R, Garbutt M, Gray M, Grolla A, Jones S, Feldmann H, Meyers A, Kabani A, Li Y, Normand S, Stroher U, Tipples GA, Tyler S, Vogrig R, Ward D, Watson B, Brunham RC, Krajden M, Petric M, Skowronski DM, Upton C, Roper RL. The Genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. doi: 10.1126/science.1085953. - DOI - PubMed
- Rota PA, Oberste MS, Monroe SS, Nix WA, Campagnoli R, Icenogle JP, Penaranda S, Bankamp B, Maher K, Chen MH, Tong S, Tamin A, Lowe L, Frace M, DeRisi JL, Chen Q, Wang D, Erdman DD, Peret TC, Burns C, Ksiazek TG, Rollin PE, Sanchez A, Liffick S, Holloway B, Limor J, McCaustland K, Olsen Rasmussen M, Fouchier R, Gunther S, Osterhaus AS, Drosten C, Pallansch MA, Anderson LJ, Bellini WJ. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.1085952. - DOI - PubMed
- Ng ML, Tan SH, See EE, Ooi EE, Ling AE. Proliferative growth of SARS coronavirus in Vero E6 cells. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:3291–3303. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19505-0. - DOI - PubMed
- Li M, Moore WJ, Vasilieva N, Sui J, Wong SK, Berne MA, Somasundaran M, Sullivan JL, Luzuriaga K, Greenough TC, Choe H, Farzan M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426:450–454. doi: 10.1038/nature02145. - DOI - PMC - PubMedShow all 26 references
Publication types
- Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
MeSH terms
- Ammonium Chloride / pharmacology
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2
- Animals
- Antiviral Agents / pharmacology*
- Chlorocebus aethiops
- Chloroquine / pharmacology*
- Fluorescent Antibody Technique, Indirect
- Glycosylation
- Membrane Glycoproteins / metabolism
- Peptidyl-Dipeptidase A / metabolism
- SARS Virus / drug effects*
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome / drug therapy*
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome / metabolism
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome / prevention & control
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome / virology
- Spike Glycoprotein, Coronavirus
- Vero Cells
- Viral Envelope Proteins / metabolism
Substances
- Antiviral Agents
- Membrane Glycoproteins
- Spike Glycoprotein, Coronavirus
- Viral Envelope Proteins
- spike glycoprotein, SARS-CoV
- Ammonium Chloride
- Chloroquine
- Peptidyl-Dipeptidase A
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2
Related information
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
COPYRIGHTS
Copy & Paste the link above for Yandex translation to Norwegian.
WHO and WHAT is behind it all ? : >
The bottom line is for the people to regain their original, moral principles, which have intentionally been watered out over the past generations by our press, TV, and other media owned by the Illuminati/Bilderberger Group, corrupting our morals by making misbehavior acceptable to our society. Only in this way shall we conquer this oncoming wave of evil.
Commentary:
Administrator
HUMAN SYNTHESIS
All articles contained in Human-Synthesis are freely available and collected from the Internet. The interpretation of the contents is left to the readers and do not necessarily represent the views of the Administrator. Disclaimer: The contents of this article are of sole responsibility of the author(s). Human-Synthesis will not be responsible for any inaccurate or incorrect statement in this article. Human-Synthesis grants permission to cross-post original Human-Synthesis articles on community internet sites as long as the text & title are not modified